meiosis 1 vs meiosis 2|Difference Between Meiosis 1 and Meiosis 2 : Tagatay Meiosis I and II, as well as mitosis, have the same five five stages: prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. With the stages in meiosis I, the primary difference lies in prophase I, which is much longer than either its meiosis II or mitosiscounterparts, and is in fact the stage a cell . Tingnan ang higit pa Blockchain is a shared, immutable ledger that facilitates the process of recording transactions and tracking assets in a business network. An asset can be tangible (a house, car, cash, land) or intangible (intellectual property, patents, copyrights, branding).
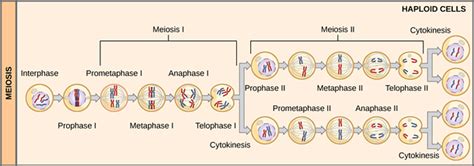
meiosis 1 vs meiosis 2,Meiosis I and II, as well as mitosis, have the same five five stages: prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. With the stages in meiosis I, the primary difference lies in prophase I, which is much longer than either its meiosis II or mitosiscounterparts, and is in fact the stage a cell . Tingnan ang higit paIn premeiotic interphase, chromosomes are duplicated and other proteins are produced that are needed for meiosis. This is the . Tingnan ang higit paMeiosis I contributes significantly to genetic diversity, which is vital to the adaptation and evolution of a species. The first event in meiosis I that contributes is crossing over, which allows genes from either parent to exchange, changing the genetic . Tingnan ang higit pa

Meiosis II is very similar to mitosis. Aside from the four phases being analogous to those in mitosis, the ploidy also remains unchanged . Tingnan ang higit paLearn how meiosis reduces chromosome number by half in two rounds of cell division. Meiosis I separates homologous chromosomes by crossing over, while meiosis II separates sister chromatids.
Learn the difference between meiosis I and meiosis II, the two phases of chromosomal reduction in eukaryotic cells. Find out . Meiosis 2 is similar to the mitotic cell division, equalizing the number of chromosomes in a parent cell produced at meiosis 1 and .
Understand the different meiosis stages and explore meiosis 1 vs meiosis 2, such as the ploidy of daughter cells. Learn the different meiosis phases in order. Updated: 11/21/2023meiosis 1 vs meiosis 2 Difference Between Meiosis 1 and Meiosis 2 Learn about meiosis, the process of cell division that reduces the number of chromosomes in sexually-reproducing organisms. Compare meiosis I and meiosis II, and how they differ from .Learn the difference between meiosis I and meiosis II, the two stages of cell division that produce gametes. See diagrams, definitions, and examples of meiosis and related terms.
Meiosis includes two phases, called meiosis I and meiosis II, which occur in sequence. Meiosis I produces two haploid daughter cells with unique chromatids , .
Learning Objectives. By the end of this section, you will be able to do the following: Describe the behavior of chromosomes during meiosis, and the differences between the first and .
Difference Between Meiosis 1 and Meiosis 2In contrast to meiosis I, meiosis II resembles a normal mitosis. In some species, cells enter a brief interphase, or interkinesis, before entering meiosis II. Interkinesis lacks an .The proteins are released when the cell enters anaphase I, so that the homologous chromosomes can be separated. Query 4.1.1 4.1. 1. Figure 4.1.1 4.1. 1: Meiosis is a process in which a diploid cell divides into 4 haploid cells. At the end of Meiosis there are four genetically different cells.
Meiosis is the process in eukaryotic, sexually-reproducing animals that reduces the number of chromosomes in a cell before reproduction. Many organisms package these cells into gametes, such .meiosis 1 vs meiosis 2Meiosis I. Meiosis is preceded by an interphase consisting of G 1, S, and G 2 phases, which are nearly identical to the phases preceding mitosis. The G 1 phase (the “first gap phase”) is focused on cell growth. During the S phase—the second phase of interphase—the cell copies or replicates the DNA of the chromosomes. Finally, in the G .Specifically, meiosis creates new combinations of genetic material in each of the four daughter cells. These new combinations result from the exchange of DNA between paired chromosomes. Such .For example, diploid human cells contain 23 pairs of chromosomes including 1 pair of sex chromosomes (46 total), half of maternal origin and half of paternal origin. Meiosis produces haploid gametes (ova or sperm) that contain one set of 23 chromosomes. When two gametes (an egg and a sperm) fuse, the resulting zygote is once again diploid, with .
meiosis. Meiosis is a type of cell division that reduces the number of chromosomes in the parent cell by half and produces four gamete cells. This process is required to produce egg and sperm . Meiosis is a type of cell division that reduces the chromosome number by half (2n to n), leading to the formation of four non-identical daughter cells. It is crucial for sexual reproduction in eukaryotes. Meiosis involves two divisions, so it’s typically broken down into meiosis I and meiosis II.Comparing mitosis and meiosis. Mitosis and meiosis are two different types of cell division. Mitosis occurs in somatic cells and results in two identical daughter cells with a diploid (2n) number of chromosomes. This process is essential for growth and repair in the body. On the other hand, meiosis occurs in germ cells and produces four non .

Meiosis Consists of a Reduction Division and an Equational Division. Two divisions, meiosis I and meiosis II, are required to produce gametes (Figure 3). Meiosis I is a unique cell division that .La meiosis 1 es una división celular compleja que implica la formación de bivalentes y la separación de cromosomas homólogos, mientras que la meiosis 2 es una división más simple que implica la separación de cromátides hermanas. La meiosis 1 también implica la formación de quiasmas, lo que permite una mezcla de material genético . Mitosis vs. Meiosis. Mitosis and meiosis are both types of cell division. Mitosis is the process by which most cells in the body divide, involves a single round of cell division, and produces two identical, . The process of meiosis is divided into 2 parts, meiosis 1 and 2. Each part consists of 4 phases (prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase), which is similar to mitosis by being comprised of four .Phases of meiosis II. Meiosis II is a process that helps cells divide and create gametes, which are needed for sexual reproduction. It starts with prophase II, where the nuclear envelope dissolves and chromosomes condense. Then, in metaphase II, chromosomes line up along the cell's middle. During anaphase II, sister chromatids separate and move . Ed Reschke/Getty Images. There are two stages or phases of meiosis: meiosis I and meiosis II. Before a dividing cell enters meiosis, it undergoes a period of growth called interphase. At the end of the meiotic process, four daughter cells are produced. G1 phase: The period prior to the synthesis of DNA.
They are caused by nondisjunction, which occurs when pairs of homologous chromosomes or sister chromatids fail to separate during meiosis. The risk of nondisjunction increases with the age of the parents. Nondisjunction can occur during either meiosis I or II, with different results ( Figure 17.5.2 17.5. 2 ). Meiosis Clearly Explained and Simplified. -- Mitosis Video: https://goo.gl/uf6hh4-- DNA Replication Video: https://goo.gl/sugAhv-- Transcription & Translatio.
1.Meiosis 1 has five phases: prophase 1, metaphase 1, anaphase 1, telophase 1 and interphase while meiosis 2 has varying stages depending on the organism. 2.Meiosis 1 recombines genes on the daughter cells produced while in meiosis 2 chromosomes are divided into these daughter cells. 3.Both substages of meiosis occur from days to weeks.While both meiosis 1 and meiosis 2 can experience nondisjunction events, there are some key differences between the two. **Timing:** Nondisjunction in meiosis 1 occurs during the initial division, while in meiosis 2, it occurs during the second division. **Resulting Cells:** In meiosis 1, the resulting cells will have an unequal distribution of .
meiosis 1 vs meiosis 2|Difference Between Meiosis 1 and Meiosis 2
PH0 · What is the Difference Between Meiosis I and Meiosis II?
PH1 · Meiosis review (article)
PH2 · Meiosis I vs Meiosis II
PH3 · Meiosis I and Meiosis II: What is their Difference?
PH4 · Meiosis 2: Definition, Stages, Meiosis 1 vs Meiosis 2
PH5 · Meiosis 1 vs. Meiosis 2
PH6 · Meiosis
PH7 · Difference Between Meiosis 1 and Meiosis 2
PH8 · Difference Between Meiosis 1 and Meiosis 2
PH9 · 3.1.2: The Process of Meiosis
PH10 · 11.2.2: Meiosis II